Any force can be broken down into components along a specific direction or axis, the broken component is called projection of the force along that specific direction or axis. The projection can help us to analyze how much of the force is influencing motion or stress in a particular direction.
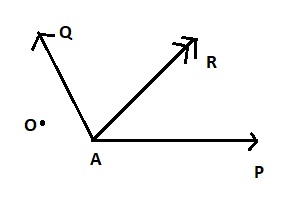
Let us consider two force P, Q and α is an angle between them.
Then the projection of P on Q = (P.Q)/Q=PQcosα /Q=Pcosα
and the projection of Q on P = (P.Q)/P=PQcosα /P=Qcosα where P and Q are magnitude of the force P and Q respectively.

From △OAC, cosα=OA/OC ⇒OA = OC cosα ⇒projection of P on Q = Pcosα
and from △OBD,
cosα=OB/OD ⇒OB = OD cosα ⇒projection of Q on P = Qcosα
In a physical context, the projection is useful in determining how much of the force contributes to deformation or movement along a certain line or plane. For instance, in resolving forces along inclined planes, the projections help us separate the force into parallel and perpendicular components.
Uses of projection of a force:
The projection of a force is essential in many areas of engineering, mathematics, physics and mechanics because it help us to simplify the complex force systems into manageable components. Some uses of the projection of a force are Analyzing Motion on Inclined Planes,Calculating Work Done by a Force,
Structural Analysis and Load Distribution, Torque and Rotational Motion,Electrical and Magnetic Force Analysis, Resolving Forces in Multi-Directional Systems, Determining Normal and Tangential Forces,
Fluid Dynamics and Aerodynamics